Fundamentally, office space types can be subdivided into four categories:
Office space types
Office cells have a floor area of 10 to 50 m2 and a room depth of up to 5,5 m. They are intended for one or two persons. The working areas and the visual task areas are located close to the window and usually sufficiently provided with daylight and supplementary artificial lighting – most often from luminaire rows parallel to the window. The rooms are usually ventilated naturally or partially air-conditioned. Provision of electrical and communication technology installations is done via window ducts, and less frequently via underfloor ducts. The cell office is still the most prevalent type of office.
Group offices range from 50 to 300 m2 in floor space and are populated by up to 25 people. Room depth can be up to 18 m, which is why the rooms are usually air-conditioned and only feature natural lighting in the zones close to windows. Central zones in rooms with windows only on one side feature continuous artificial lighting. The room-based artificial lighting must facilitate flexible workstation arrangements (desk groups) in the room. Flexible and movable lighting systems – possibly in addition to room-based basic lighting – can be advantageous (see also section "Lighting concepts"). Group offices with room depths of up to 8 m can be regarded as cell offices strung together when it comes to lighting and ventilation.
Combination officesare composed of one-person office spaces at the windows separated by room-height dividers. A common area most often located at the centre, which contains meeting and waiting areas as well as office appliances and file archives separated by partitions and furniture. The individual offices have a floor space of up to 12 m2, a room depth of up to 5 m and a room width of up to 3 m. They are usually naturally ventilated and illuminated, with supplementary artificial lighting. The common room is usually air-conditioned and features continuous artificial lighting – sometimes with varying lighting levels according to the area. Electrical and communication technology installations for the individual offices are located in window ducts, the common room is supplied via underfloor ducts.
Open plan offices, developed as a modern office concept in the 1960s, seem to be experiencing a renaissance. They may lack the privacy of the combination office working areas, but the flexibility akin to that of a group office as well as the advantages of common rooms as featured in combination offices are appreciated. Medium-height partitions and cabinets transform a floor space between 400 and 1 200 m2 into flexible working areas for up to 100 persons. Full air-conditioning and continuous artificial lighting of indoor areas as well as installation ducts underneath the floor or in suspended ceilings are further typical characteristics of open plan offices. The artificial lighting is usually either a room-based or area-related system which can be supplemented by individual workstation luminaires (see also section "Lighting concepts"). This ensures the required flexibility of working area arrangements.
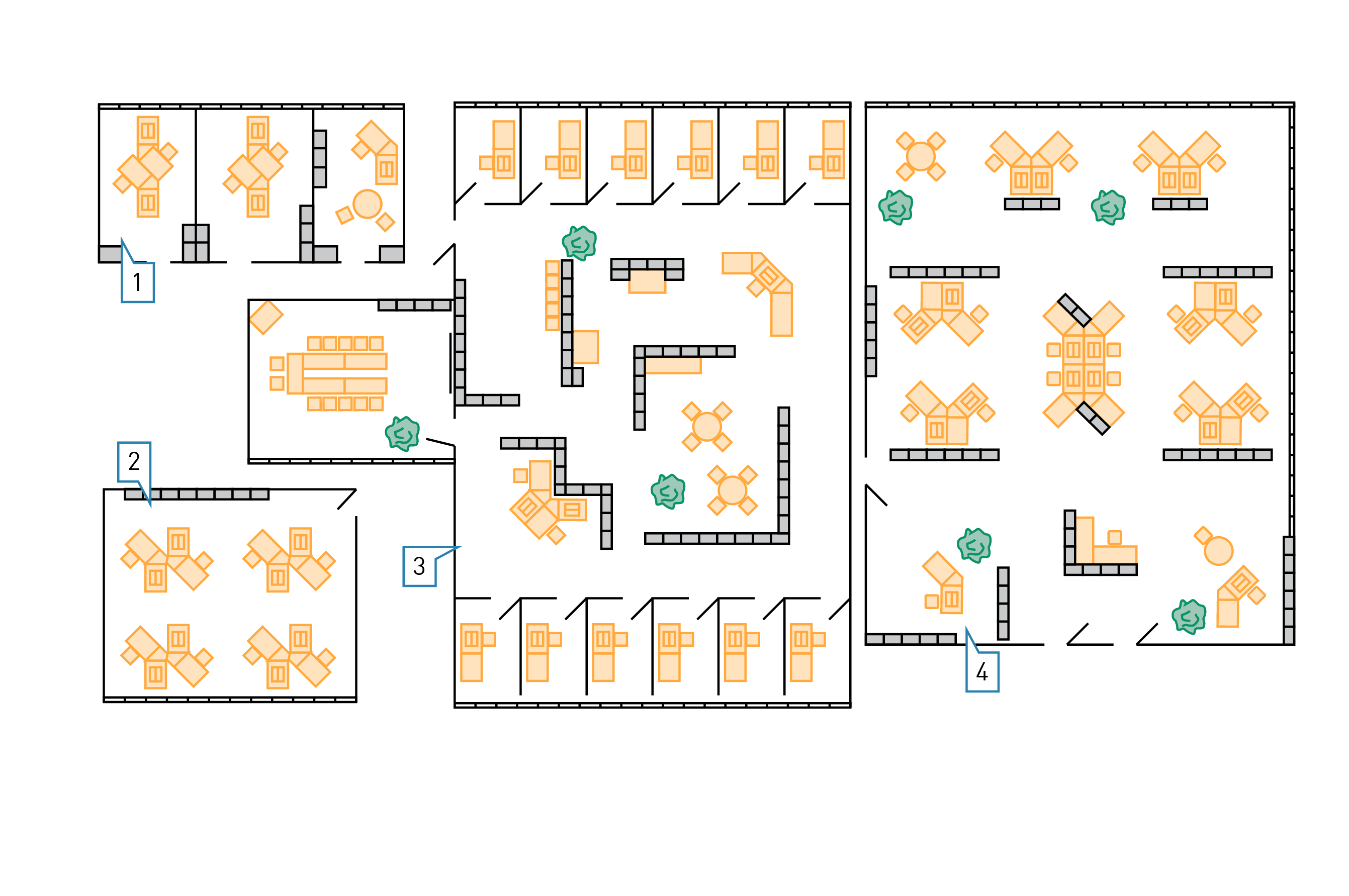
Figure 3.89: Office room types
1. Cell office
2. Group office
3. Combination office
4. Open-plan office